Amphitrite: Queen of the Seas
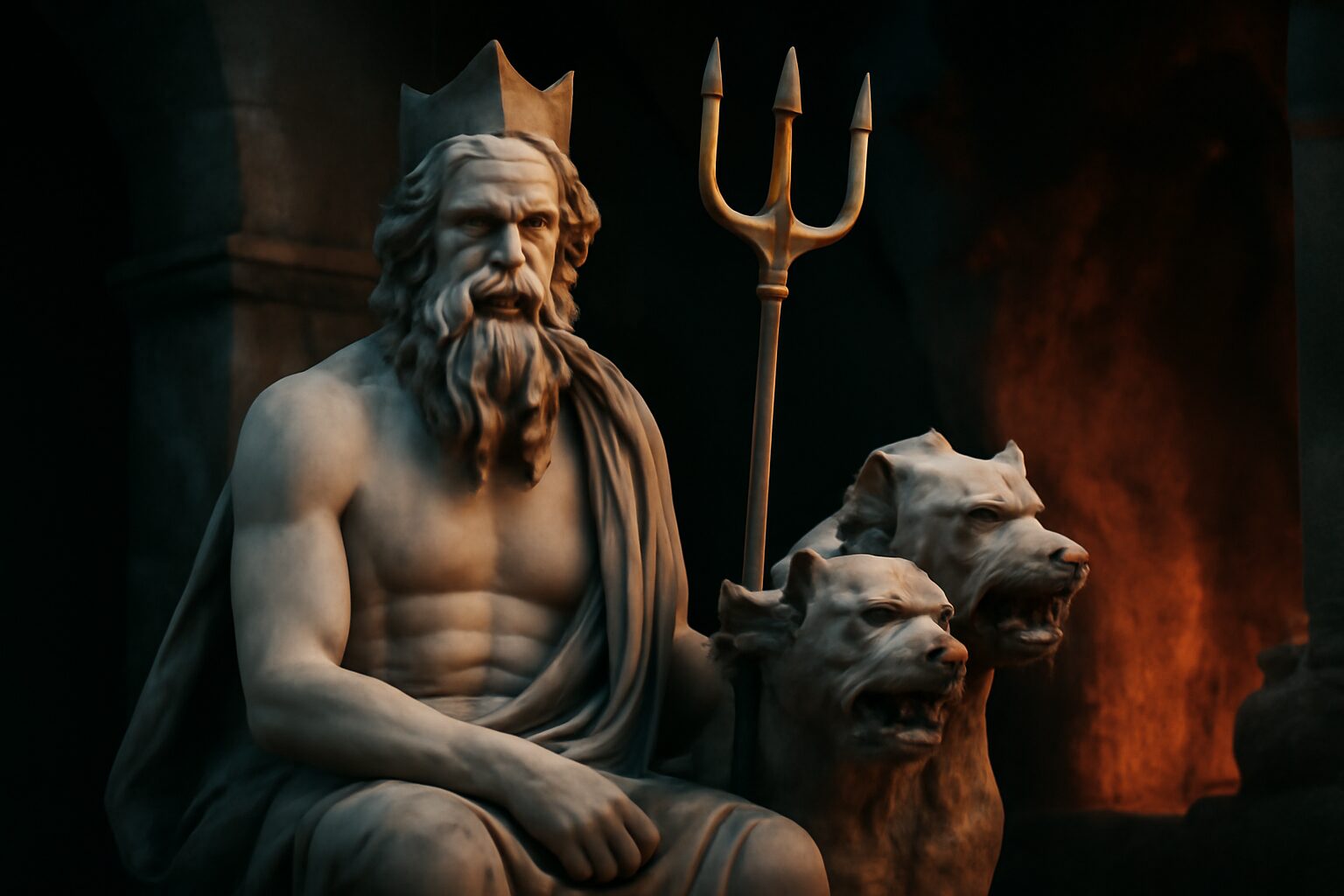
In Greek mythology, Amphitrite reigns as the majestic goddess of the sea and the wife of Poseidon, the mighty god of the oceans. Originally a Nereid—one of the fifty sea nymphs born to the ancient sea deities Nereus and Doris—Amphitrite became the personification of the Mediterranean Sea and a symbol of the ocean's untamed beauty.
Mythology and Origins
Amphitrite's story begins in the depths of the Aegean Sea, where she lived among her sisters, the Nereids, known for their grace and connection to sailors. Unlike some deities who sought the limelight, Amphitrite was initially reluctant to marry Poseidon. According to myth, she fled to the farthest reaches of the ocean to avoid his advances. However, the clever dolphin god Delphin eventually persuaded her to return, earning his place among the stars as the constellation Delphinus.
Once united with Poseidon, Amphitrite became the queen of the sea, ruling alongside her husband. She bore him several children, including Triton, the famous merman who carried a conch shell trumpet, and Rhode, the nymph associated with the island of Rhodes.
Powers and Symbolism
As a sea goddess, Amphitrite commanded the waves and marine life, often depicted riding a chariot pulled by hippocampi—mythical sea horses. She was revered by sailors and coastal communities, who prayed to her for safe voyages and calm waters. Her presence was believed to bring fertility to the seas, ensuring abundant fish and prosperous trade.
Art and literature often portray Amphitrite with a regal crown, holding a trident or a fisherman's net, symbolizing her dominion over the ocean. Unlike Poseidon, whose temperament mirrored the sea's storms, Amphitrite embodied its serene and nurturing aspects, though she could unleash its fury when angered.
Relationships and Legacy
Amphitrite's marriage to Poseidon was central to her mythology, though she was sometimes overshadowed by her more famous husband. Despite this, she remained a powerful figure in her own right, worshiped in coastal cities like Corinth and Sparta. Her Roman counterpart, Salacia, carried similar attributes in later mythology.
Though not as frequently mentioned as other Olympians, Amphitrite's influence persisted in maritime traditions and art. She represented the sea's dual nature—both life-giving and destructive—a reminder of humanity's enduring fascination with the ocean's mysteries.
Alternative Names for Amphitrite
God Name: Salacia (Roman)
In Roman mythology, Amphitrite is equated with Salacia, the goddess of saltwater and the depths of the ocean. She is the consort of Neptune, much like Amphitrite is the consort of Poseidon in Greek mythology.
God Name: Halosydne (Greek (Epithet))
An epithet for Amphitrite meaning 'sea-born' or 'sea-nurtured,' highlighting her connection to the ocean. This name emphasizes her divine origin and dominion over the sea.
God Name: Kymopoleia (Greek (Epithet))
Though sometimes considered a separate figure, Kymopoleia is occasionally linked to Amphitrite as an epithet or daughter, meaning 'wave-walker,' reflecting her mastery over the ocean's waves.
Tales about Amphitrite
Amphitrite and the River God Achelous
In the early days of her reign as Queen of the Sea, Amphitrite often encountered territorial disputes between her oceanic domain and the freshwater realms. One such conflict arose with Achelous, the mighty river god who sometimes allowed his currents to encroach upon her shores. Rather than engage in battle, Amphitrite—wisdom flowing through her like the tides—invited Achelous to a council at the mouth of his river, where saltwater met fresh.
A Truce Forged in Currents
Amphitrite arrived gracefully, her presence calming the waves, while Achelous emerged with the powerful rush of his waters. She spoke of balance: "Your rivers give life to the land, and my seas connect the world. Let us define our boundaries so both may thrive." Achelous, impressed by her diplomacy, agreed. Together, they sculpted the riverbanks and established estuaries as zones of shared influence. This accord brought prosperity to coastal communities and became a model for harmony between sea and river deities. The success of this agreement was noted by other water deities including Thelxiope, Scamander, and Triteia, who often sought Amphitrite's counsel in their own aquatic negotiations.
Amphitrite and the Dolphin Herald Delphin
Before her marriage to Poseidon, Amphitrite resided in the distant depths, wary of the god's advances. Poseidon, desperate to win her favor, sent numerous envoys, but none could sway her—until Delphin, a clever dolphin, volunteered. Delphin dove into the abyss, his sleek form cutting through the dark waters with purpose.
The Persuasion of the Deep
Delphin found Amphitrite among coral gardens, her sorrow casting a pall over the vibrant marine life. Instead of pleading Poseidon's case outright, he shared tales of the ocean's wonders that only a queen could unite: migrating whales singing hymns to the moon, and tidal patterns that danced with the stars. Moved by his poetic vision, Amphitrite saw the potential in a partnership that would elevate the seas. She returned with Delphin, rewarding his loyalty by placing him among the stars as the constellation Delphinus, a eternal reminder of the bond forged that day. This celestial honor inspired other sea deities like Peisinoe and Molpe, while even Eupheme, the spirit of praise, celebrated this harmonious union.
Frequently Asked Questions
Who is Amphitrite in Greek mythology?
Amphitrite is a sea goddess in Greek mythology, known as the wife of Poseidon, the god of the sea. She is often depicted as a queen of the ocean and the mother of sea creatures like Triton.
What is Amphitrite the goddess of?
Amphitrite is primarily the goddess of the sea, specifically the Mediterranean Sea. She represents the calm and nurturing aspects of the ocean, as well as its vastness and mystery.
Why is Amphitrite important in Greek mythology?
Amphitrite is important because she symbolizes the power and beauty of the sea. As Poseidon's wife, she plays a key role in sea-related myths and represents the balance between the ocean's tranquility and its storms.
How is Amphitrite related to modern culture?
Amphitrite's legacy lives on in modern culture through references in literature, art, and even marine conservation efforts. Her name is sometimes used to symbolize the ocean's majesty and environmental importance.
What can we learn from the story of Amphitrite?
Amphitrite's story teaches us about the ancient Greeks' respect for the sea and its unpredictable nature. It also highlights themes of partnership, as she and Poseidon ruled the ocean together, showing balance in power.