Orphne: The Shadowy Nymph of the Underworld
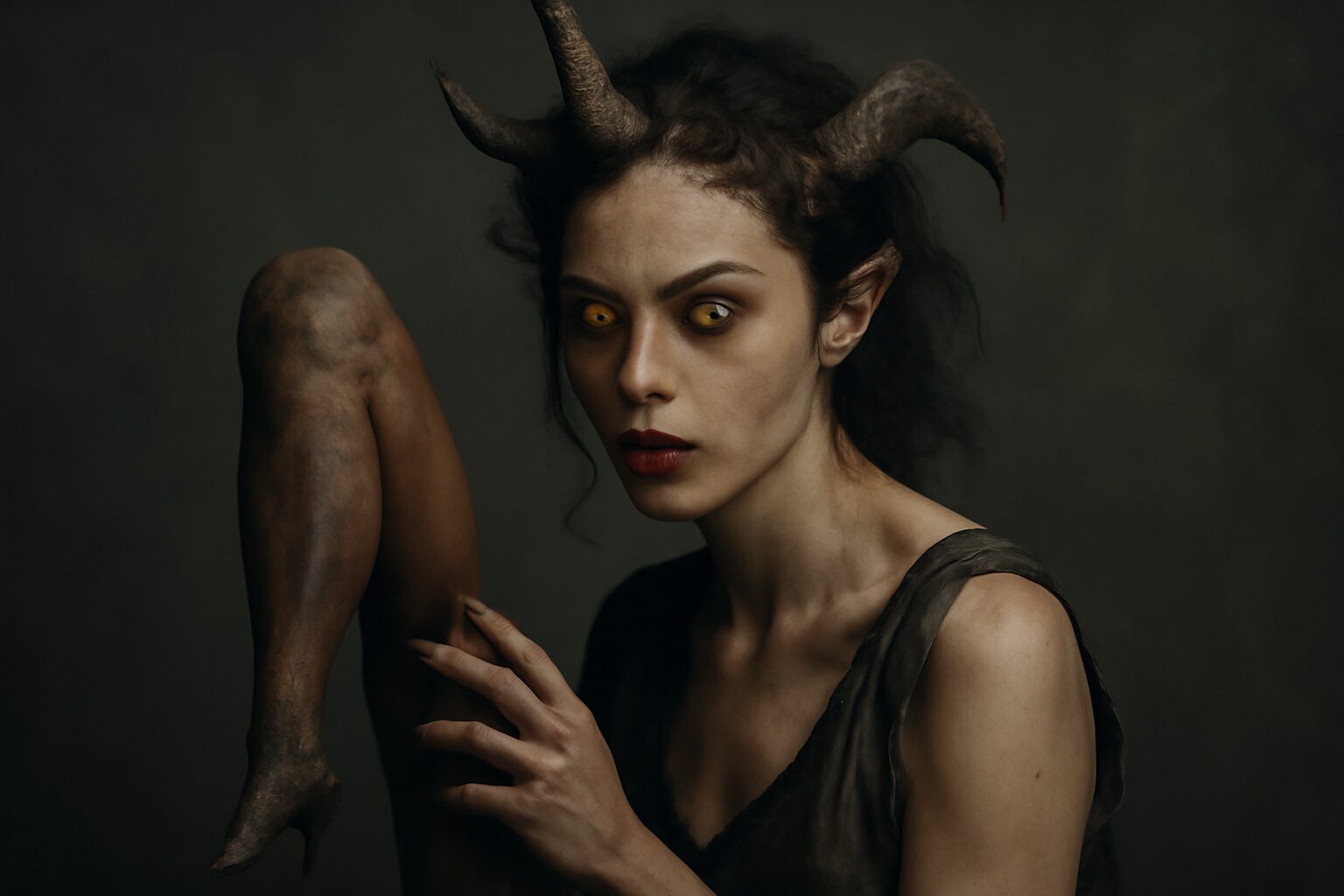
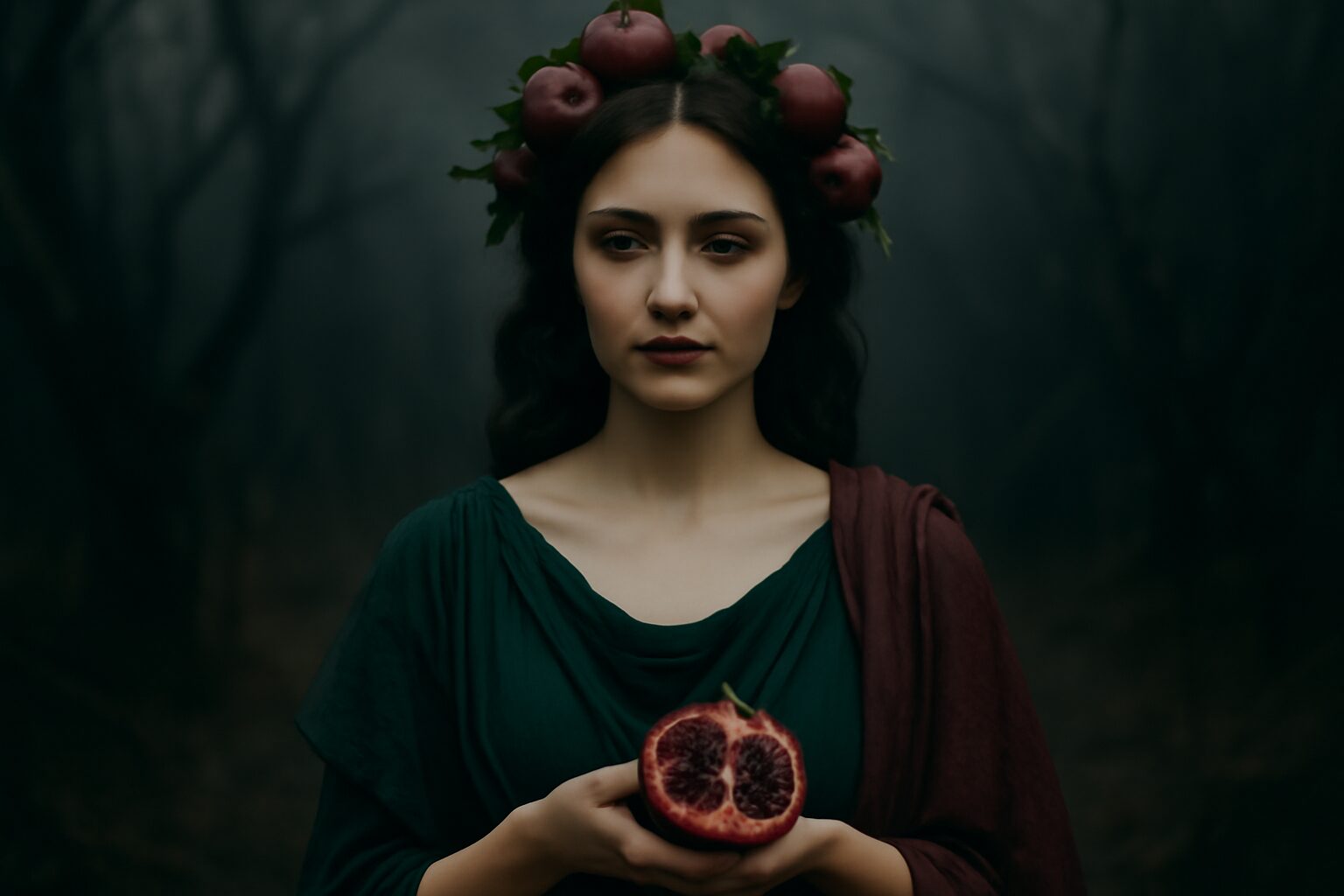
In the shadowy depths of Greek mythology, Orphne (meaning "darkness" or "night") was a mysterious nymph associated with the Underworld. Often called Gorgyra in some traditions, she was a lesser-known but fascinating figure who dwelled in the realm of Hades and Persephone.
Mythology and Role
Orphne was primarily known as a naiad nymph of the Underworld's hidden springs and rivers. Unlike most nymphs who inhabited the surface world, she made her home in the caverns and waterways beneath the earth. Her most significant myth involves her relationship with the river god Acheron, one of the five rivers of the Underworld.
With Acheron, Orphne bore a son named Ascalaphus, who would later play a tragic role in Persephone's myth. Some versions suggest she may have also been associated with the Cocytus, the river of wailing, emphasizing her connection to sorrow and darkness.
Family Connections
Orphne's lineage varies in different sources. Some accounts make her the daughter of Oceanus and Tethys, placing her among the primordial water deities. Others suggest she was one of the many children of Nyx (Night), which would explain her shadowy nature.
Her son Ascalaphus became the Underworld's orchard keeper and famously witnessed Persephone eating pomegranate seeds, ensuring her annual return to Hades. For this revelation, Demeter punished Ascalaphus by turning him into a screech owl.
Symbolism and Significance
Orphne represents the hidden waters of the Underworld - those mysterious, life-giving springs that existed even in the realm of death. Her name and nature connect her to concepts of darkness, obscurity, and the unseen forces beneath the earth's surface.
As a figure who bridges the world of nymphs and chthonic deities, Orphne symbolizes the interconnectedness of all waters in Greek cosmology - from mountain springs to ocean depths to the rivers of Hades. Her story reminds us that even in the land of the dead, the life-giving power of water persists.
Alternative Names for Orphne
God Name: Gorgyra (Greek)
Gorgyra is an alternative name for Orphne in Greek mythology. It is derived from the word 'gorgos' meaning 'dreadful' or 'terrible,' reflecting her chthonic nature as a nymph of the underworld.
God Name: Caligo (Roman)
In Roman mythology, Caligo is sometimes associated with Orphne. The name means 'darkness' or 'mist,' aligning with her role as a shadowy underworld figure.
God Name: Styx (Greek)
Though primarily the name of the river in the underworld, Styx is occasionally linked to Orphne as a personification of the underworld's darkness and mystery.
Tales about Orphne
Orphne and Hades: The Nymph of the Underworld
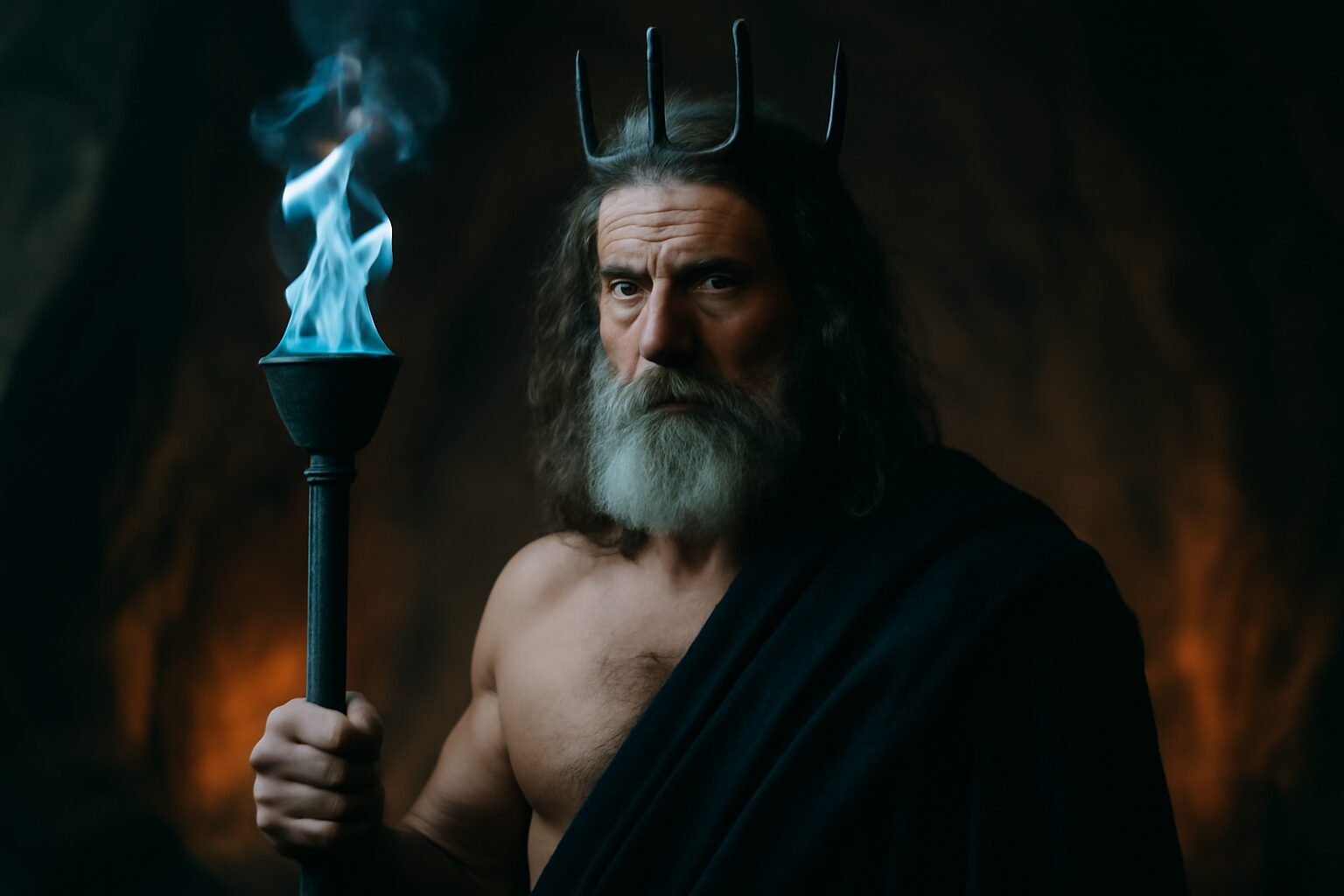
Deep within the shadowy realm of the Underworld, where the river Cocytus weeps and the Cerberus guards the gates, dwelled Orphne, a nymph of darkness and obscurity. She was the consort of the river god Acheron, and together they embodied the melancholy and mystery of the subterranean world. It was in these depths that she caught the attention of Hades, the stern ruler of the dead.
Hades, often isolated in his majestic palace, found solace in Orphne's serene presence. Unlike the boisterous gods of Olympus, she understood the weight of eternity and the silence of souls. One evening, as he wandered near the banks of the Styx, he offered her a rare gift: a grove of black poplars, whose leaves whispered secrets of the departed. This grove became her sanctuary, a place where even the lord of the Underworld would retreat to ponder the balance between life and death.
Their bond, though seldom spoken of in myths, symbolized the hidden tenderness beneath Hades' formidable exterior. Through Orphne, the darkness of the Underworld gained a touch of grace, reminding all that even in the realm of the dead, there is beauty and connection.
Orphne and Asclepius: A Glimpse of Healing
In another tale, Orphne's influence extended beyond the shadows when she encountered Asclepius, the god of medicine and healing. Asclepius, in his quest to master the art of reviving the dead, ventured into the Underworld to study the boundaries between life and demise. It was there that he met Orphne, who served as a guide through the labyrinthine gloom.
With her intimate knowledge of the underworld rivers and spirits, Orphne showed Asclepius the delicate threads that tether the soul to the body. She revealed to him the healing properties of plants that grew in the dim light near Acheron's banks, which could soothe even the most tormented of spirits. Though Asclepius' ambitions would later anger Zeus, his time with Orphne left a lasting impression, infusing his practices with a deeper respect for the natural cycle of life and death.
This encounter highlights Orphne's role as a bridge between worlds—a figure of darkness who nonetheless contributed to the pursuit of light and healing.
Frequently Asked Questions
Who is Orphne in Greek mythology?
Orphne is a minor nymph or goddess in Greek mythology associated with the underworld. Her name means 'darkness' or 'night,' and she is sometimes considered the mother of Ascalaphus, a figure connected to Hades' realm.
What are Chthonic deities in Greek mythology?
Chthonic deities are gods or spirits associated with the underworld, earth, or the afterlife in Greek mythology. They include figures like Hades, Persephone, and Hecate, and were often worshiped with different rituals than the Olympian gods.
Why are Chthonic deities important in Greek mythology?
Chthonic deities represent important aspects of life like death, rebirth, and the mysteries of the underworld. They remind us that the ancient Greeks saw death as a natural part of existence and developed rituals to honor these powerful forces.
How is Orphne connected to other underworld figures?
Orphne is sometimes described as a companion or wife of Acheron, a river god of the underworld. Through her son Ascalaphus, she's connected to Persephone's myth, as he witnessed Persephone eating pomegranate seeds in the underworld.
What can we learn from Chthonic deities today?
These deities teach us about how ancient cultures understood life's cycles. Their stories explore themes we still grapple with today - mortality, the afterlife, and humanity's relationship with nature's darker aspects.