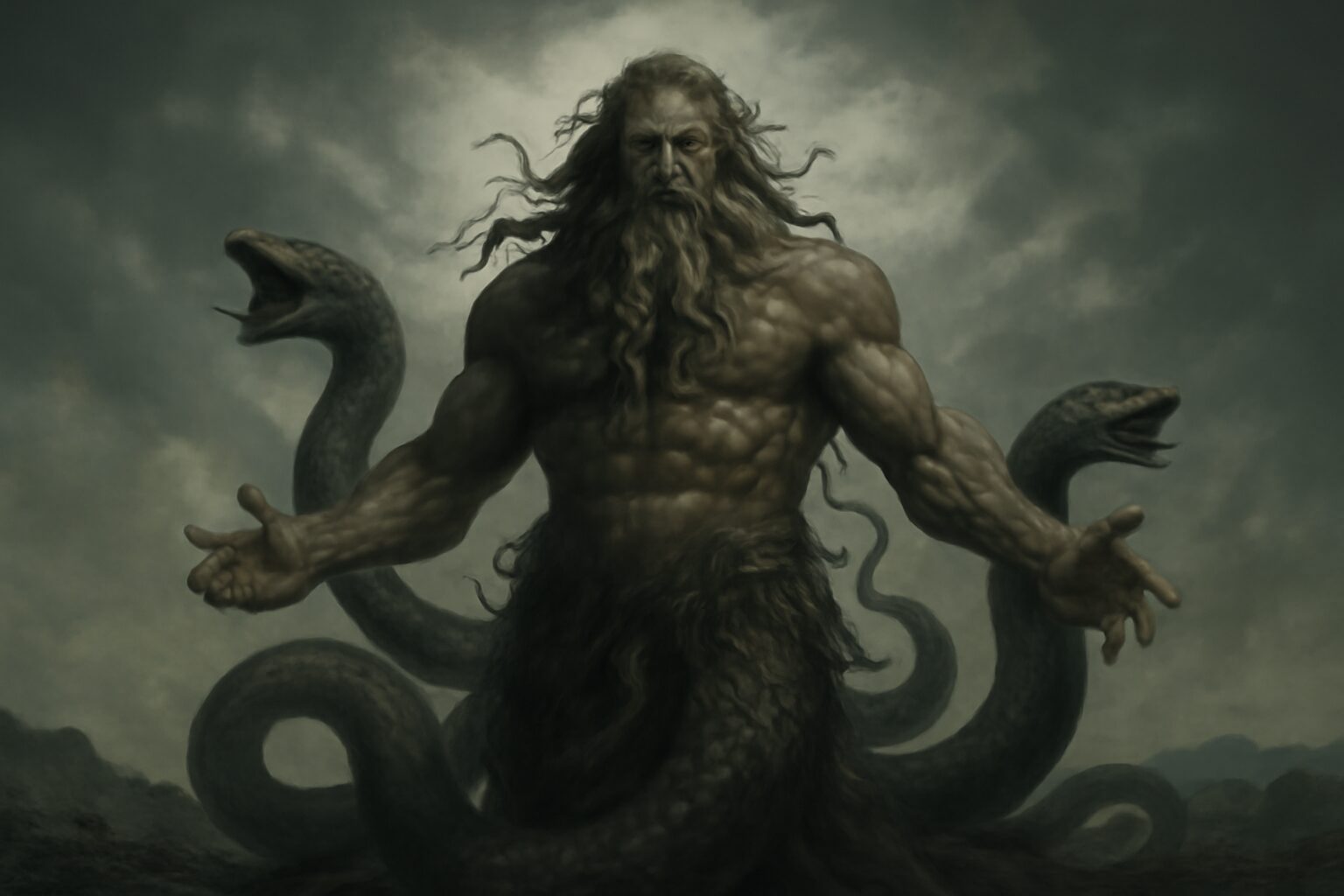
Steropes: The Lightning-Forging Cyclops
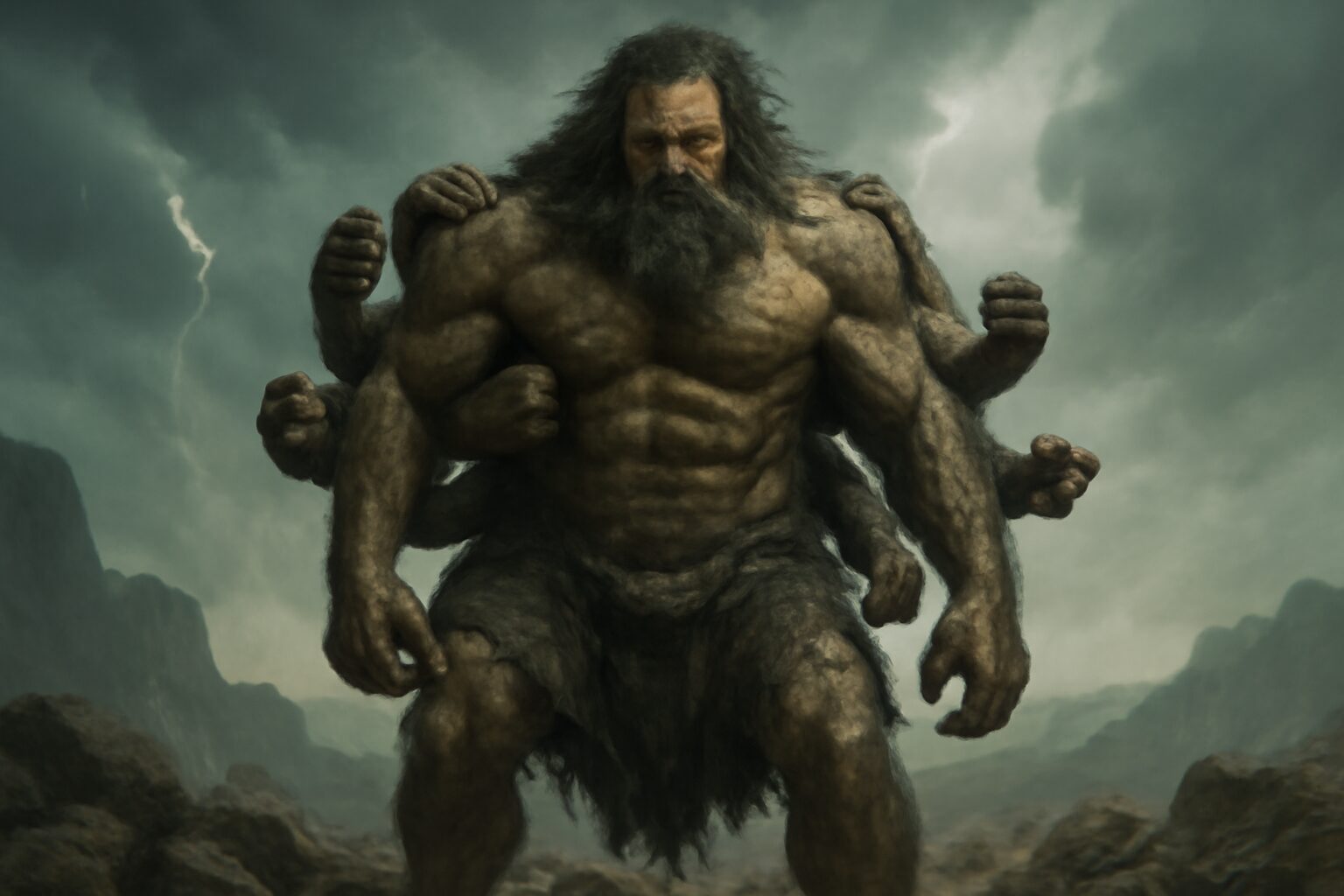
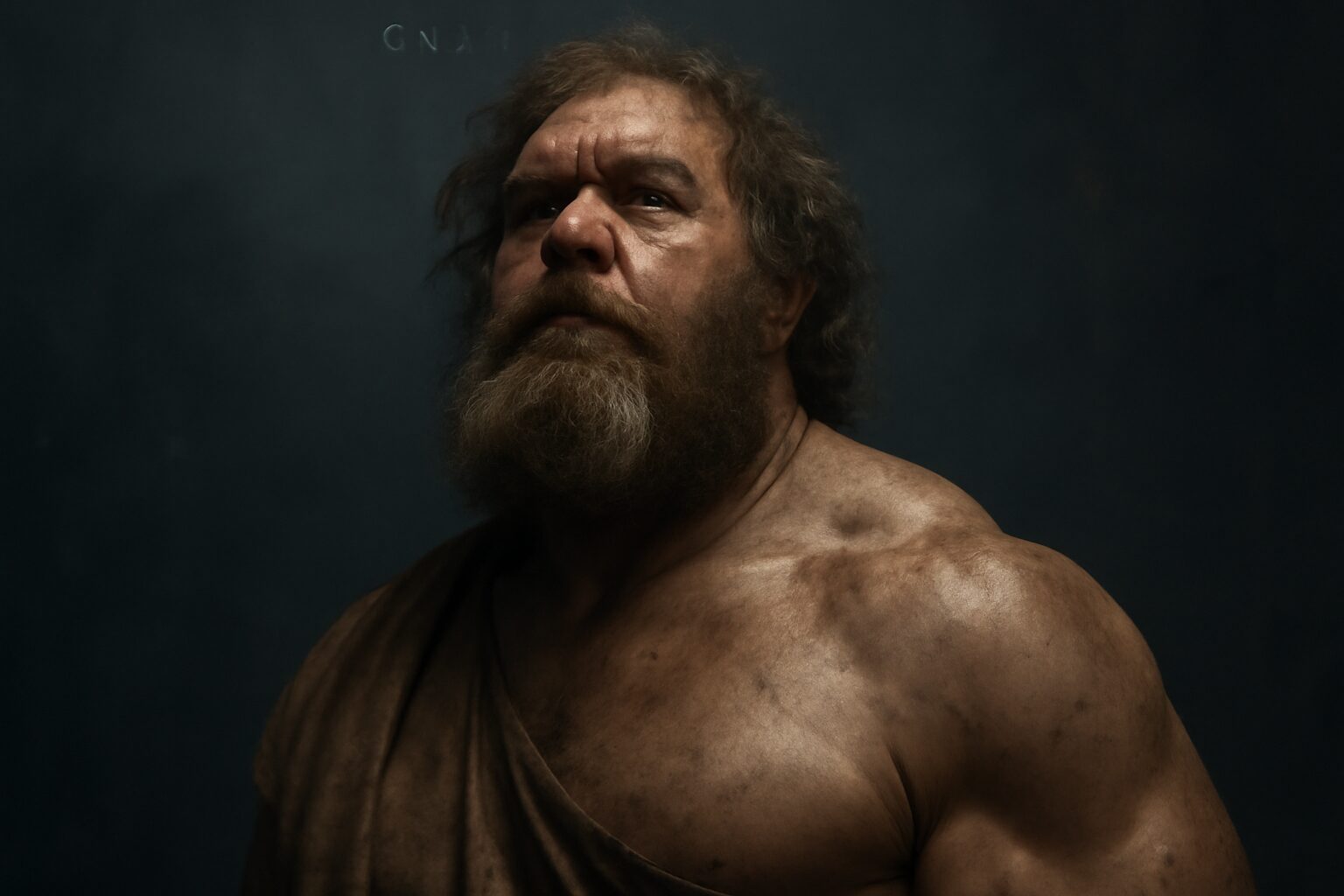
In Greek mythology, Steropes (meaning "Lightning" or "Thunderbolt") was one of the three primordial Cyclopes—giant one-eyed beings known for their incredible strength and craftsmanship. Alongside his brothers Brontes ("Thunder") and Arges ("Bright"), Steropes played a crucial role in shaping the divine weapons of the gods.
Mythology and Origins
Steropes and his brothers were the children of Uranus (Sky) and Gaia (Earth), making them siblings to the Titans and the Hecatoncheires. Fearing their power, Uranus imprisoned them in Tartarus, but they were later freed by Zeus during the Titanomachy—the great war between the Olympians and the Titans.
As master blacksmiths, the Cyclopes crafted Zeus's legendary thunderbolts, Poseidon's trident, and Hades' helm of darkness. Steropes, in particular, was associated with forging the lightning bolts that became Zeus's signature weapon, symbolizing his dominion over the skies.
Powers and Significance
Unlike the later, more savage Cyclopes of Homer's Odyssey, Steropes and his brothers were revered as divine artisans. Their craftsmanship was unmatched, and their creations were instrumental in Zeus's victory over the Titans. The thunderbolts forged by Steropes were not just weapons but symbols of divine authority and cosmic order.
In some versions of the myth, the Cyclopes were later killed by Apollo in retaliation for Zeus striking his son, Asclepius, with one of their lightning bolts. However, their legacy endured as the archetypal forgers of the gods' most powerful tools.
Relationships and Cultural Impact
Steropes' lineage tied him to the earliest forces of the cosmos, and his work directly influenced the balance of power among the Olympians. His name became synonymous with the raw, untamed energy of storms, reflecting the Greeks' awe of natural forces.
Though less famous than figures like Zeus or Hercules, Steropes' role highlights the importance of craftsmanship and divine favor in Greek mythology. His thunderbolts remained a recurring symbol of Zeus's might, appearing in countless myths and artistic depictions.
Alternative Names for Steropes
God Name: Astrapaios (Greek)
An alternative epithet for Steropes, meaning 'Lightning Maker,' highlighting his association with thunder and lightning.
God Name: Fulgor (Roman)
A Roman equivalent or epithet for Steropes, derived from 'fulgur,' meaning lightning, emphasizing his role as a lightning-wielder.
God Name: Brontes (Greek)
Sometimes conflated with Steropes as one of the Cyclopes, Brontes means 'Thunderer,' another name emphasizing his storm-related powers.
God Name: Arges (Greek)
Another Cyclops sibling of Steropes, whose name means 'Bright' or 'Shining,' occasionally used interchangeably in myths.
Tales about Steropes
The Forging of the Thunderbolt
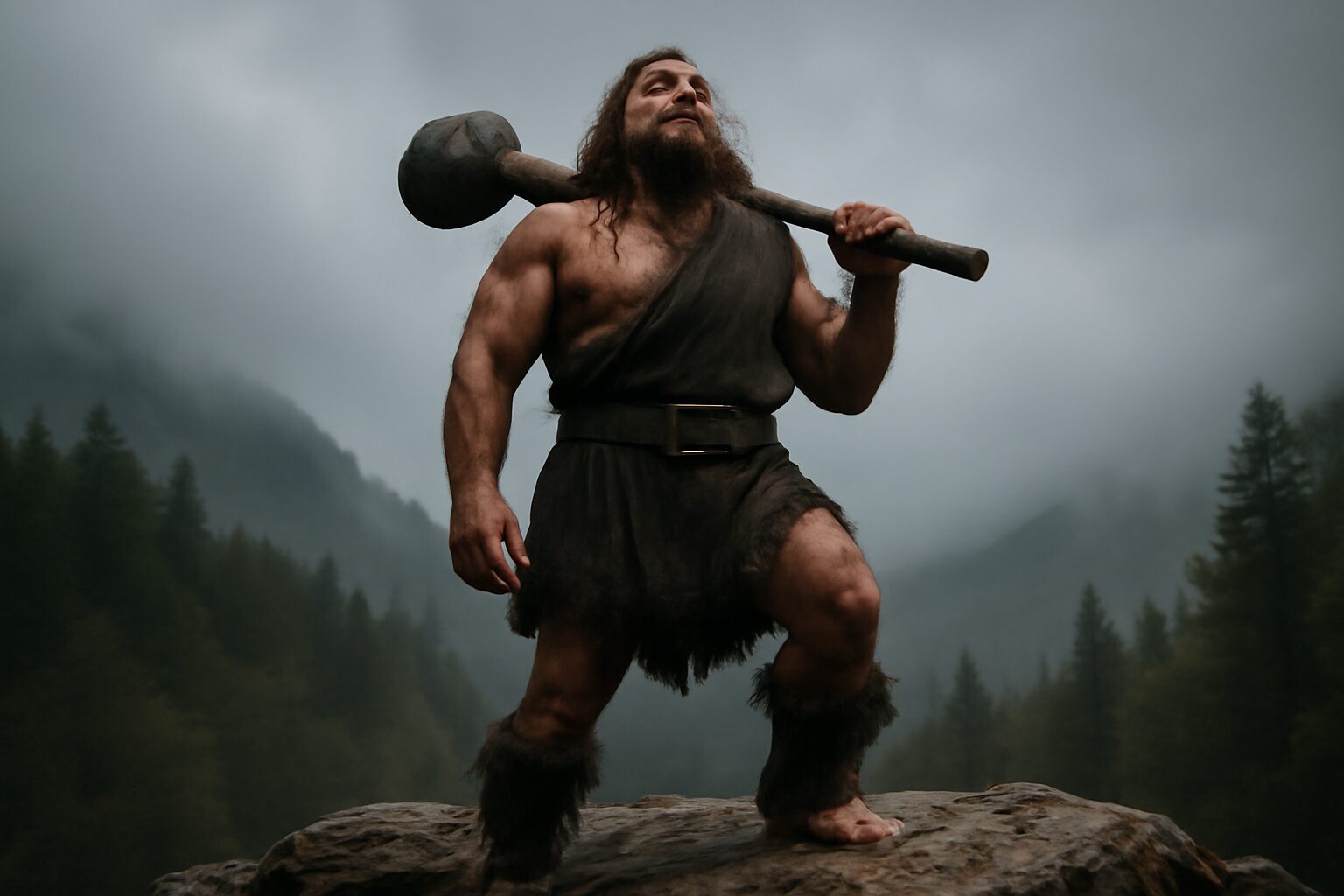
In the fiery depths beneath Mount Etna, Steropes toiled alongside his Cyclopean brethren. Their mighty hammers struck the anvils in a rhythmic symphony, crafting divine weapons for the gods. One day, Zeus descended into their forge, his brow furrowed with concern. The Titans threatened to overthrow Olympus, and he needed a weapon of unparalleled power.
Steropes, whose name means "Lightning," took up the challenge. With sparks flying like miniature stars, he channeled the raw energy of the storm into a single, magnificent bolt. As he hammered, the very air crackled with electricity. When he presented the thunderbolt to Zeus, its brilliance illuminated the entire cavern. Zeus grasped it, and with a triumphant roar, he unleashed its power, securing his reign. From that day, the thunderbolt became his symbol of authority, forged by the skilled hands of Steropes.
The Gift of Healing Light
During the Gigantomachy, the great war between gods and giants, many Olympians suffered grievous wounds. Iaso, the goddess of healing, worked tirelessly but found her remedies insufficient for the divine injuries. Desperate, she sought out Steropes in his volcanic forge.
Recognizing the urgency, Steropes devised a ingenious solution. Using his mastery over light and fire, he crafted a luminous crystal that could focus and amplify healing energies. He imbued it with the pure essence of sunlight, creating a device that could seal even the most terrible wounds. Iaso used this gift to great effect, mending the injuries of gods like Ares and Artemis. The alliance between the forge's lightning and the gentle touch of healing turned the tide, showcasing how even the most violent forces could be harnessed for restoration and peace.
Frequently Asked Questions
Who is Steropes in Greek mythology?
Steropes is one of the Cyclopes, a group of one-eyed giants in Greek mythology. He is known for forging Zeus's thunderbolts and helping the gods in their battle against the Titans.
What are the Gigantes in Greek mythology?
The Gigantes, or Giants, were a race of enormous and powerful beings born from Gaia (Earth) and the blood of Uranus. They fought against the Olympian gods in a great battle called the Gigantomachy.
Why are the Cyclopes and Gigantes important in Greek myths?
The Cyclopes and Gigantes play key roles in the struggles between gods and primordial forces. The Cyclopes helped Zeus gain power, while the Gigantes' battle with the gods symbolized the triumph of order over chaos.
What lessons can we learn from the myths of the Gigantes?
The Gigantomachy teaches about the conflict between old and new orders, showing how even powerful forces like the Giants can be overcome by unity and strategy, as seen in the gods' victory.
How do the myths of Steropes and the Gigantes apply today?
These myths reflect timeless themes like the struggle between chaos and order, the importance of craftsmanship (like the Cyclopes' forging), and how legends explain natural phenomena (e.g., earthquakes attributed to Giants).