Phoebe: The Radiant Leucippides
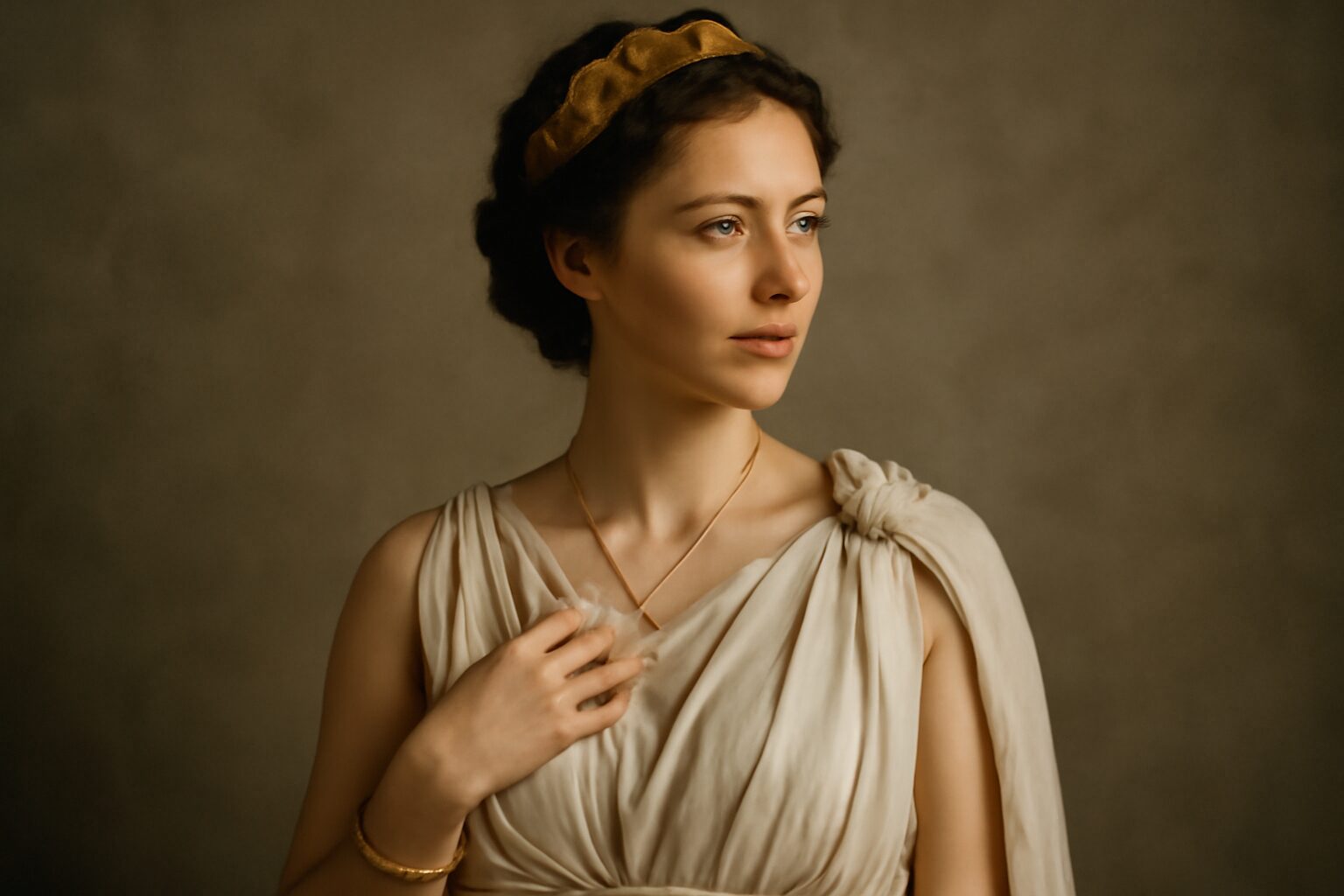
In Greek mythology, Phoebe was one of the Leucippides, a pair of sisters known for their beauty and divine lineage. Alongside her sister Hilaeira, Phoebe was worshiped in Sparta and played a significant role in local myths, particularly those involving the Dioscuri—Castor and Pollux.
Mythology and Origins
Phoebe and Hilaeira were daughters of Leucippus, a legendary king of Messenia, and were sometimes associated with the moon goddess Artemis due to their names—Phoebe meaning "the bright one" and Hilaeira "the gentle one." Their abduction by the Dioscuri is one of the most famous myths surrounding them. Castor and Pollux, smitten by the sisters, carried them off, leading to a violent conflict with their betrothed cousins, the Apharetidae.
Role and Worship
As part of Spartan tradition, the Leucippides were honored in religious rites, particularly in connection to marriage and fertility. Their myth symbolized the transition from maidenhood to marriage, making them important figures in Spartan society. Temples and festivals celebrated their legend, reinforcing their status as divine protectors of women.
Powers and Symbolism
Though not major Olympian deities, Phoebe and Hilaeira were revered for their celestial associations. Phoebe’s name linked her to light and radiance, suggesting a connection to the moon or dawn. Their myth also intertwined with the stars, as the Dioscuri were later immortalized as the constellation Gemini.
Significance in Greek Mythology
The story of Phoebe and Hilaeira reflects themes of love, rivalry, and divine intervention. Their abduction by the Dioscuri highlights the intersection of mortal and divine destinies, while their worship in Sparta underscores their cultural importance. Though lesser-known than Olympian goddesses, the Leucippides remain fascinating figures in Greek myth, embodying both grace and the turbulent nature of ancient legends.
Alternative Names for Phoebe (Leucippides)
God Name: Phoibe (Greek)
An alternative spelling of Phoebe in Greek, often used in poetic or older texts.
God Name: Leucippides (Roman)
In Roman mythology, the Leucippides (meaning 'daughters of Leucippus') were sometimes associated with or identified as Phoebe and her sister Hilaeira, particularly in the context of their abduction by the Dioscuri.
God Name: Dione (Greek)
In some interpretations, Phoebe is conflated with Dione, a Titaness associated with the oracle of Dodona. This connection is speculative and based on overlapping mythological roles.
God Name: Artemis (Greek)
In later traditions, Phoebe was sometimes syncretized with Artemis, particularly in her role as a moon goddess, though this is not a direct alternative name but rather a merging of identities in certain cults.
Tales about Phoebe (Leucippides)
The Rescue of Phoebe by Castor
Phoebe, one of the Leucippides, was renowned for her grace and beauty, often drawing the attention of both mortals and gods. One day, while wandering near the river Eurotas, she encountered the monstrous sea creature Scylla, who had been driven into the river by a storm. Scylla, with her ferocious dog-heads and serpentine tails, threatened to drag Phoebe into the depths. Just as Phoebe’s cries echoed through the valley, Castor, the heroic twin and horseman, arrived on his swift steed. With unmatched bravery, Castor engaged Scylla, using his spear to drive her back into the sea. Grateful, Phoebe praised Castor’s valor, and their bond grew, symbolizing the protection of purity against chaos.
Key Elements of the Tale
- Phoebe’s Vulnerability: Her innocence made her a target for Scylla’s wrath.
- Castor’s Heroism: As a deified mortal, he embodied courage and swift action.
- Symbolism: The story highlights the triumph of order over primordial terror.
Phoebe’s Alliance with Artemis
In the forests of Arcadia, Phoebe, the Leucippides maiden, sought refuge from the relentless advances of the river god Alpheus, who was determined to make her his bride. Desperate, she called upon Artemis, the virgin goddess of the hunt. Artemis, moved by Phoebe’s plight, shrouded her in a mystical mist and transformed her into a shimmering spring, hidden among the ancient oaks. Alpheus, confused and thwarted, flowed past unaware. From that day, Phoebe became a guardian of sacred waters under Artemis’s protection, and hunters would offer prayers at her spring for clarity and purity in their pursuits.
Highlights of the Encounter
- Divine Intervention: Artemis’s power provided a clever escape from Alpheus’s pursuit.
- Transformation: Phoebe’s new form as a spring symbolized eternal purity and refuge.
- Legacy: The tale reinforces Artemis’s role as a protector of maidens and nature.
Frequently Asked Questions
Who is Phoebe in Greek mythology?
Phoebe is one of the Leucippides, twin daughters of King Leucippus in Greek mythology. She and her sister Hilaeira were priestesses of Artemis and Athena, known for their beauty and their role in the myth of the Dioscuri (Castor and Pollux).
What does it mean to be a deified mortal in Greek mythology?
Deified mortals are humans who were granted godhood or divine status, often as a reward for heroic deeds, favor from the gods, or due to their lineage. This reflects the Greek belief that exceptional humans could transcend mortality.
Why are the Leucippides important in Greek myths?
The Leucippides, including Phoebe, are important because their abduction by the Dioscuri (Castor and Pollux) led to key mythological events, highlighting themes of love, conflict, and the intersection of mortal and divine worlds.
What can we learn from the story of Phoebe and the Leucippides?
Their story teaches about ancient Greek values like honor, family loyalty, and the consequences of divine intervention in human lives. It also reflects societal views on marriage and female agency in myths.
How does the concept of deified mortals apply today?
The idea of humans achieving godlike status resonates in modern hero worship (celebrities, athletes) and stories of superhumans, showing how ancient themes of exceptionalism and transcendence persist in culture.