Enyo: The Goddess of War and Destruction
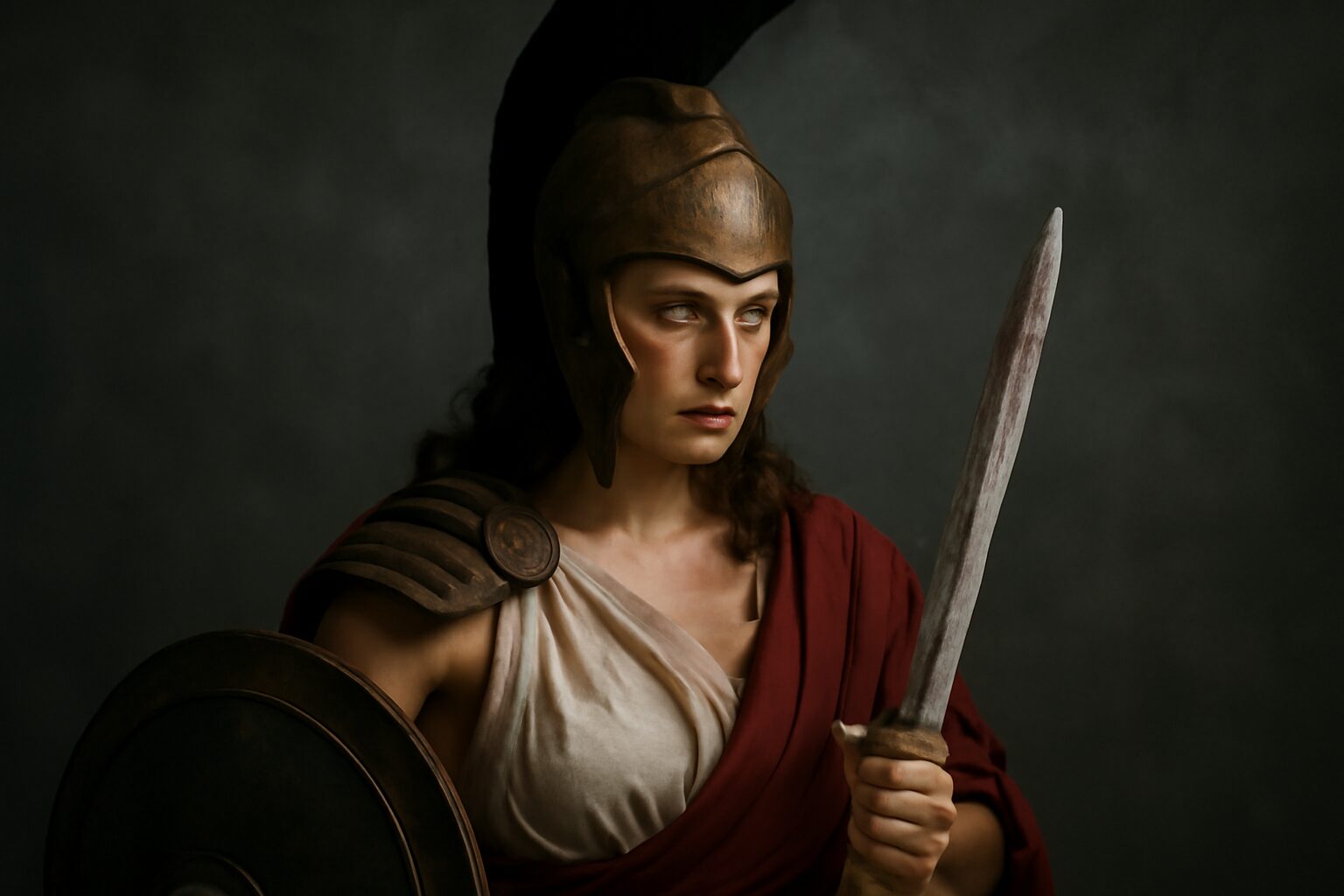
In Greek mythology, Enyo was a fierce and formidable goddess of war, often associated with bloodshed, destruction, and the chaos of battle. Her name, derived from the Greek word enyos, meaning "warlike," reflects her brutal nature. While she is sometimes overshadowed by her more famous counterpart, Ares, the god of war, Enyo played a vital role in the pantheon as a personification of the horrors of combat.
Role and Powers
Enyo was not merely a bystander in war—she was an active participant, reveling in the carnage. Ancient texts describe her as a terrifying presence on the battlefield, often accompanied by Phobos (Fear) and Deimos (Terror), the sons of Ares. She was said to delight in the destruction of cities and the slaughter of warriors, embodying the brutal and unforgiving side of war. Unlike Athena, who represented strategic warfare, Enyo symbolized the raw, unrelenting violence of battle.
Her powers extended beyond physical combat; she was also believed to incite conflict among mortals, sowing discord and chaos. Some myths suggest she had the ability to influence the outcomes of battles, ensuring devastation for those who crossed her.
Relationships and Myths
Enyo was closely linked to Ares, sometimes described as his sister, consort, or even his female counterpart. Together, they formed a terrifying duo, spreading war and destruction wherever they went. In some traditions, she is also associated with Eris, the goddess of strife, further cementing her role as a bringer of chaos.
One of the most notable myths involving Enyo is her participation in the Trojan War, where she fought alongside Ares, inciting bloodshed and terror among the warriors. She was also said to have played a role in the destruction of cities, including the fall of Troy, where her presence amplified the suffering and devastation.
Significance in Greek Mythology
Enyo’s significance lies in her representation of the darker aspects of war—uncontrolled violence, destruction, and the inevitable suffering it brings. While gods like Athena and Ares were worshiped for their martial prowess, Enyo served as a reminder of war’s brutal reality. Her worship was not as widespread as other deities, but she was invoked in times of conflict, particularly by those who sought to harness her destructive power.
In later traditions, Enyo was sometimes conflated with Bellona, the Roman goddess of war, further solidifying her legacy as a symbol of warfare’s devastation. Though she may not be as well-known as other Olympians, Enyo’s presence in Greek mythology underscores the ancient Greeks' complex understanding of war—not just as a means of glory, but as a force of utter ruin.
Alternative Names for Enyo
God Name: Bellona (Roman)
Bellona is the Roman equivalent of the Greek goddess Enyo. She is the goddess of war and is often associated with Mars, the Roman god of war. Bellona was worshiped in Rome and was considered a significant deity in Roman military culture.
God Name: Enyalios (Greek)
Enyalios is an alternative name or epithet for Enyo in Greek mythology. It is sometimes used interchangeably with Enyo or as a separate but closely related war deity. The name Enyalios is also associated with Ares, the Greek god of war.
God Name: Enyo (Greek)
Enyo is a variant spelling of Enyo, the Greek goddess of war. The name is used interchangeably in various ancient texts and myths, often depicting her as a fierce and destructive force in battle.
Tales about Enyo
Enyo and Ares: The War Council
During the Trojan War, Ares, the god of war, summoned his sister and companion Enyo to strategize the turning of the tide. As the embodiment of war and destruction, Enyo arrived cloaked in the smoke of burning cities, her presence intensifying the chaos on the battlefield. Together, they orchestrated a series of brutal assaults, with Enyo sowing discord among the Greek ranks and Ares leading the Trojan charge. Their collaboration turned the plains of Troy into a maelstrom of blood and fury, demonstrating how closely aligned destruction and strategic warfare truly are.
The Aftermath
Though the war eventually concluded, the partnership of Ares and Enyo left an indelible mark on mortal and divine memory, a testament to the terrifying power of coordinated conflict.
Enyo and Phobos: The Fear Campaign
In a campaign to dismantle a defiant city-state, Enyo enlisted Phobos, the personification of fear and panic. While Enyo led the physical destruction—shattering walls and inciting violence—Phobos swept through the populace, embedding deep, irrational terror. Citizens, gripped by phantom dread, turned on each other, and soldiers fled at mere whispers of approaching doom. Their combined efforts crumbled the city’s spirit before a single sword was drawn, showcasing how fear can be as destructive as any weapon.
The Legacy of Dread
The alliance between Enyo and Phobos became a chilling lesson on the psychology of warfare, where panic proved to be the ultimate catalyst for collapse.
Frequently Asked Questions
Who is Enyo in Greek mythology?
Enyo is the Greek goddess of war, often associated with destruction and bloodshed. She is sometimes considered a companion or counterpart to Ares, the god of war, and is known for her fierce and violent nature in battles.
Why is Enyo important in Greek mythology?
Enyo represents the brutal and chaotic aspects of war, contrasting with the strategic side often attributed to Athena. Her importance lies in embodying the sheer violence and devastation of conflict, reminding us of war's destructive power in Greek myths.
What can we learn from the stories about Enyo?
Enyo's stories highlight the ancient Greeks' understanding of war's dual natureu2014both as a necessary part of human history and as a source of immense suffering. Her myths serve as cautionary tales about the consequences of unchecked aggression.
How does Enyo compare to other war deities like Ares or Athena?
While Ares represents the chaotic and bloodthirsty side of war, and Athena symbolizes strategic warfare and wisdom, Enyo focuses purely on the carnage and havoc of battle. She is often depicted as more relentless and less strategic than Athena.
Are there any modern references or influences of Enyo today?
Enyo's legacy lives on in modern culture through references in literature, video games, and media that explore themes of war and destruction. Her name is sometimes used to symbolize unrelenting conflict or chaos in fictional works.