Praxidike: The Goddess of Exact Justice
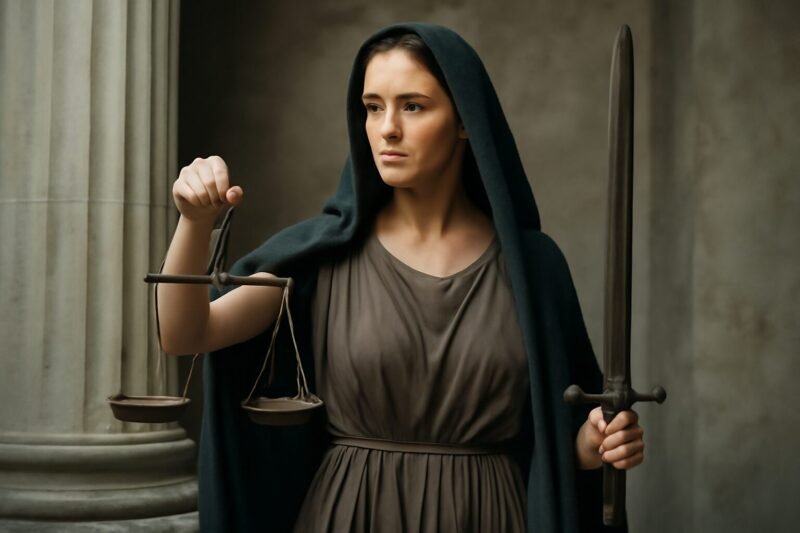
In the vast pantheon of Greek deities, Praxidike stands as a lesser-known but powerful figure representing exact justice and retribution. Her name, derived from the Greek words praxis (action) and dike (justice), encapsulates her role as the enforcer of moral and legal order.
Mythology and Role
Praxidike was often worshiped alongside her daughters, Arete (virtue) and Homonoea (concord), forming a triad that upheld righteousness in human affairs. Unlike the more famous goddesses of justice, such as Themis or Dike, Praxidike was specifically associated with the execution of justice—ensuring that oaths were kept, wrongs were avenged, and moral balance was maintained.
Powers and Symbolism
As a divine arbiter, Praxidike possessed the authority to exact punishment on oath-breakers and wrongdoers. She was sometimes invoked in legal oaths, as her presence was believed to guarantee that justice would be served without mercy or leniency. Though she lacked the widespread temples of Olympian gods, her influence was feared—those who swore falsely in her name risked her wrath.
Her symbolism is less documented than that of major deities, but she may have been associated with scales or a sword, much like other justice-related figures. Some sources suggest she was worshiped in secretive or localized cults, particularly in Boeotia, where justice deities held significant importance.
Relationships and Significance
Praxidike was sometimes considered the daughter of Zeus, linking her to the king of gods' role as a divine judge. Alternatively, she was seen as a primordial force, emerging from the cosmic order itself. Her daughters, Arete and Homonoea, extended her influence into human virtue and societal harmony, reinforcing her connection to ethical conduct.
While not as prominent as other justice deities, Praxidike’s role was crucial in Greek thought—she embodied the inescapable nature of justice, ensuring that no transgression went unanswered. Her legacy endures as a reminder of the ancient Greeks' belief in moral accountability, where even the gods demanded righteous action.
Alternative Names for Praxidike
God Name: Praxidice (Greek)
An alternative spelling of Praxidike, found in some ancient Greek texts, emphasizing the goddess's role in exacting justice.
God Name: Praxidica (Roman)
The Romanized version of Praxidike, adapted to fit Latin linguistic conventions while retaining the original meaning related to justice and retribution.
God Name: Areia (Greek)
An epithet sometimes associated with Praxidike, linking her to Ares (Areia meaning 'of Ares'), suggesting a warlike aspect of justice or vengeance.
God Name: Themis (Greek)
Though Themis is a distinct goddess of divine law and order, Praxidike is sometimes conflated or associated with her due to overlapping domains of justice and retribution.
Tales about Praxidike
Praxidike and Ares: The Judgment of War
In the midst of a brutal conflict between two city-states, the cries of the fallen reached the ears of Praxidike, the goddess of exacting justice. She descended to the battlefield, her presence bringing a momentary hush to the chaos. There, she encountered Ares, the god of war, who reveled in the bloodshed.
Praxidike confronted Ares, demanding an account of the conflict's origins. Ares, amused, claimed that war needed no justification—it was its own purpose. But Praxidike, unwavering, insisted that even war must adhere to principles of justice. She summoned the spirits of the slain, hearing their testimonies.
Through her meticulous inquiry, Praxidike uncovered that one city had provoked the war through deceit and broken oaths. She delivered her judgment: the aggressor city would face divine retribution, its leaders stripped of power. Ares, though initially dismissive, acknowledged her authority, and from that day, even the god of war respected the balance she enforced.
Praxidike and Hermes: The Oath-Breaker's Fate
A wealthy merchant, known for his cunning, had sworn a solemn oath to repay a debt to a humble farmer. When the time came, the merchant denied the agreement, relying on his influence to avoid consequences. The farmer, despairing, prayed to Praxidike for justice.
Praxidike, hearing the plea, enlisted the help of Hermes, the messenger god and guide of souls. Together, they devised a plan. Hermes, disguised as a traveler, approached the merchant and engaged him in conversation, skillfully extracting the truth about the broken oath.
With the evidence gathered, Praxidike appeared before the merchant, her gaze piercing his deceit. She declared that his wealth would vanish until he made amends. Hermes, using his cunning, ensured the merchant's assets were mysteriously misplaced, leaving him destitute until he honorably repaid the farmer. The duo’s collaboration became a legend, illustrating that no oath-breaker could escape divine retribution.
Frequently Asked Questions
Who is Praxidike in Greek mythology?
Praxidike is a lesser-known Greek goddess or spirit (daimon) associated with exacting justice and vengeance. Her name means 'executor of justice,' and she was often invoked to ensure oaths were kept and wrongs were punished.
What is the significance of Praxidike in Greek mythology?
Praxidike represents the concept of divine justice and retribution in Greek mythology. She symbolizes the idea that justice will eventually be served, even if it takes time, reinforcing moral and ethical behavior in ancient Greek society.
Are there any myths or stories about Praxidike?
Praxidike doesn't feature prominently in major Greek myths, but she is sometimes mentioned as the mother of Ktesios, a minor deity associated with household prosperity. Her role was more abstract, representing the enforcement of justice rather than appearing in narratives.
How does Praxidike relate to other Greek deities of justice?
Praxidike is closely related to other justice-related deities like Dike (goddess of moral justice) and Nemesis (goddess of retribution). While Dike represents cosmic order and Nemesis focuses on revenge, Praxidike embodies the execution of justice, especially in oaths and agreements.
What can modern people learn from Praxidike's concept?
Praxidike's concept reminds us that justice and accountability are timeless values. While we no longer worship these deities, the idea that actions have consequences and that justice should be served remains relevant in modern legal and ethical systems.